引言
- 之所以写这篇文章,由于公司项目要实现手动上传本地日志到服务器,刚开始的想法是直接跳转到指定的文件夹,然后手动点击上传选中的文件。但是由于Google它的这个API不好使了,无法跳转到指定文件夹,当我设置为跳转到指定文件夹的时候,总是跳转到最近的文件夹:
//path获取具体文件所在的地址,例如返回值为/storage/sdcard0/MIUI/video/告白气球.mp4
File file = new File(path);
//获取父目录
File parentFlie = new File(file.getParent());
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_GET_CONTENT);
intent.setDataAndType(Uri.fromFile(parentFlie), "*/*");
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_OPENABLE);
startActivity(intent);
- 所以我决定写一个RcycleView列表,直接显示存储列表,然后能够点击选择文件,进行上传,又因为上传日志的时候发现,当天的日志是不断被写入了(大小一直在变化),所以无法直接上传。于是我果断创建一个新的文件夹(临时文件夹),将当天日志复制到新文件夹里面去了,然后实现了当天的日志上传。

深入理解File类
- 首先介绍File类:通俗易懂的来讲,就是文件所在的目录地址的具体实现,譬如目录地址为下面两种:
第一种:
- path为:/storage/emulated/0/Android/logs
获取File对象:
File file = new File(path);
获取logs文件夹内所有文件的名称数组:
File file = new File(path);
File[] files = new File(path);
第二种:
- path为:/storage/emulated/0/Android/logs/README.txt
获取File对象:
File file = new File(path);
获取目录文件夹的File对象和地址path:
File file = new File(path);
File fileDirectory = file.getParentFile();
String fileDirectoryPath = file.getParent();
File常用方法:
创建文件夹:
File file = null;
try {
file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.i("error:", e.getMessage());
}
删除文件夹内全部文件:
/**
* 删除指定文件夹下的所有文件
* @param directoryFile 指定文件夹 /storage/Android/directory
*/
public static void deleteDirectoryFile(File directoryFile) {
if (directoryFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = directoryFile.listFiles();
for (File i : files) {
if (i.isFile()) {
i.delete();
}
}
}
}
复制指定文件到新文件夹内:
/**
* 复制旧文件夹文件,粘贴到新文件夹下
* 执行此程序的前提条件是,已经创建了新老两个文件夹( file.mkdir()方法 )
* @param newFilePath 新文件地址 /storage/Android/new/newFile.txt
* @param oldFilePath 旧文件地址 /storage/Android/old/oldFile.txt
*/
public static void copy(String newFilePath, String oldFilePath) {
try {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(oldFilePath);
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFilePath);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while (-1 != (length = inputStream.read(buffer))) {
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
inputStream.close();
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 其中 while ( -1 != ( length = inputStream.read( buffer ) ) ) 中的 -1 是因为当读取完成的时候会返回-1
- 如果对二进制流的理解不太清楚的可以参考我的这篇文章:Android串口通信:抱歉,学会它真的可以为所欲为
代码为:这个是显示文件RecyclerView的列表,复制粘贴代码不在这个里面
代码:
package com.baoda.vending.filedemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.File;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//todo FILE_PATH :这个是你需要获取文件的地址,自己来定义
String FILE_PATH = "/storage/emulated/0/Android/logs";
private ArrayList<File> fileArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<String> fileNameArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
private Context mContext = this;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
processExtraData();
}
private void processExtraData() {
RecyclerView uploadLogsRecycleView = findViewById(R.id.fragment_upload_logs);
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if (files == null) {
return;
}
//获取文件列表内的所有文件名称的集合
for (File i : files) {
fileArrayList.add(i);
fileNameArrayList.add(i.getName());
}
LinearLayoutManager mLinearLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager
(mContext, LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL, false);
uploadLogsRecycleView.setLayoutManager(mLinearLayoutManager);
UploadLogsAdapter adapter = new UploadLogsAdapter(fileNameArrayList, mContext);
uploadLogsRecycleView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private class UploadLogsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter {
ArrayList<String> mList = new ArrayList<>();
private Context context;
private UploadLogsAdapter(ArrayList<String> mList, Context context) {
this.mList = mList;
this.context = context;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public RecyclerView.ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
MyViewHolder myViewHolder = null;
View view = View.inflate(context, R.layout.item_file, null);
//第二种获取item的View的方法,不需要传入context
// View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.item_file, parent, false);
myViewHolder = new MyViewHolder(view);
return myViewHolder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull final RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder, final int position) {
((MyViewHolder) holder).fileNameTextView.setText(mList.get(position));
((MyViewHolder) holder).detailTextView.setText(String.format(getResources().getString
(R.string.text_file_size), getReadableFileSize(fileArrayList.get(position).length())));
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mList.size();
}
class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
private TextView fileNameTextView;
private TextView detailTextView;
MyViewHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
fileNameTextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.fileNameTextView);
detailTextView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.fileDetailTextView);
}
}
}
//传入file.length大小,得出具体的存储大小
private String getReadableFileSize(long size) {
if (size <= 0) {
return "0";
}
final String[] units = new String[]{"B", "KB", "MB", "GB", "TB"};
int digitGroups = (int) (Math.log10(size) / Math.log10(1024));
return new DecimalFormat("#").format(size / Math.pow(1024, digitGroups)) + " " + units[digitGroups];
}
}
运行结果:
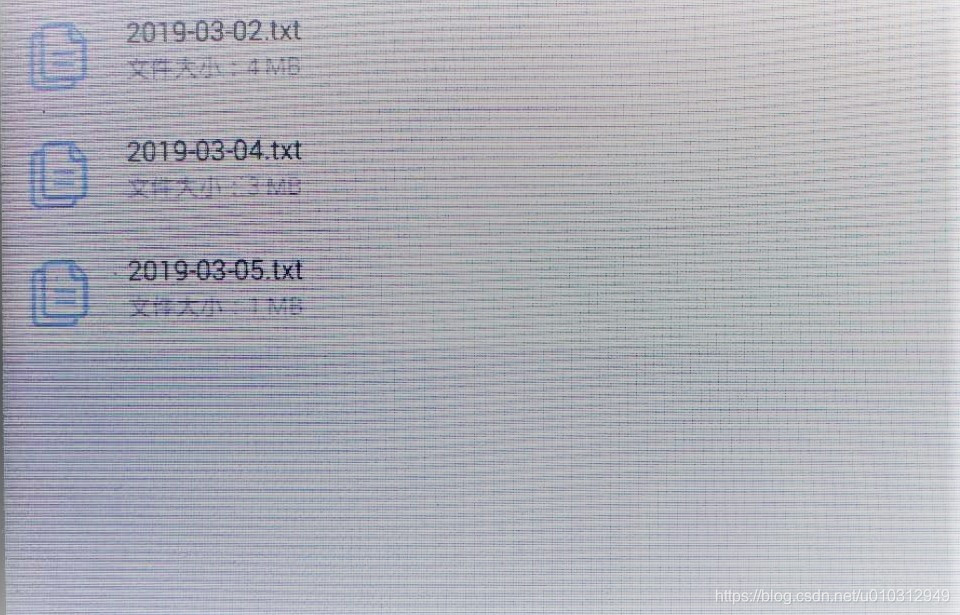
我犯的错误:
- 当时我直接将图片粘贴到drawable中,然后它大爷的直接将我的图片默认到E:\git\FileDemo\app\src\main\res\drawable-v24 导致AS一直报这个错:android.view.InflateException: Binary XML file line #0: Error inflating class ImageView
- 老实说,drawable这个玩意儿坑我不是一次两次了,比如以前每次我想放的地址都是E:\saiyao\app\src\main\res\drawable-mdpi它偏偏无数次跟我默认到其它地址,真是坑,所以直接粘贴的时候,大家就得小心了。

源代码Here:
-
Github
下载地址:!——> FileRecyclerViewDemo
